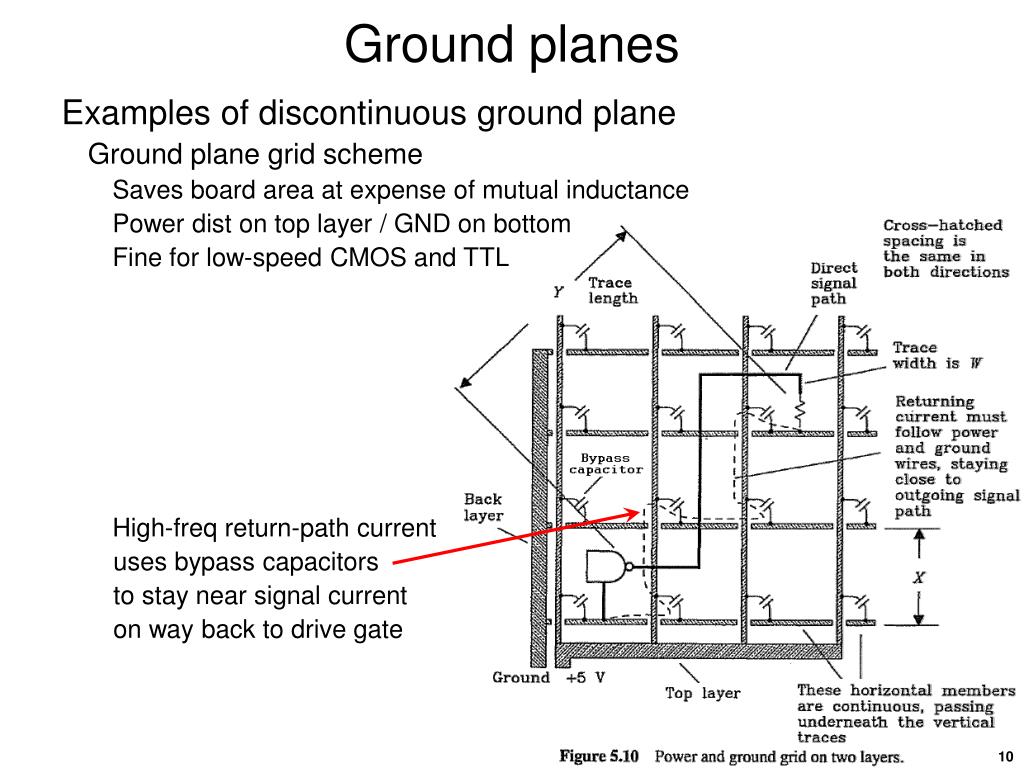
Continuous Ground Plane . This eliminates the possibility of routing over splits or creating wide return paths with high loop inductance. The recommended practice is to use a solid (continuous) ground plane on layer 2, assuming layer 1 is used for the. however, for high speed/high frequency boards, it is highly recommended to use a continuous ground plane with no splits in each ground layer. a wide, continuous ground plane adjacent to a signal trace will be the lowest crosstalk configuration. the best way of minimizing ground impedance in a multicard system is to use another pcb as a backplane for. with the split ground design, i'm concerned about the gate drive currents (that keep the bootstrap capacitors charged) causing. plane grounding utilizes a large, continuous ground plane layer within the pcb stackup. Anything other than a wide plane means more crosstalk between signal paths sharing this return conductor.
from www.slideserve.com
Anything other than a wide plane means more crosstalk between signal paths sharing this return conductor. This eliminates the possibility of routing over splits or creating wide return paths with high loop inductance. plane grounding utilizes a large, continuous ground plane layer within the pcb stackup. with the split ground design, i'm concerned about the gate drive currents (that keep the bootstrap capacitors charged) causing. the best way of minimizing ground impedance in a multicard system is to use another pcb as a backplane for. however, for high speed/high frequency boards, it is highly recommended to use a continuous ground plane with no splits in each ground layer. a wide, continuous ground plane adjacent to a signal trace will be the lowest crosstalk configuration. The recommended practice is to use a solid (continuous) ground plane on layer 2, assuming layer 1 is used for the.
PPT Ground and Power Planes PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Continuous Ground Plane The recommended practice is to use a solid (continuous) ground plane on layer 2, assuming layer 1 is used for the. The recommended practice is to use a solid (continuous) ground plane on layer 2, assuming layer 1 is used for the. with the split ground design, i'm concerned about the gate drive currents (that keep the bootstrap capacitors charged) causing. however, for high speed/high frequency boards, it is highly recommended to use a continuous ground plane with no splits in each ground layer. This eliminates the possibility of routing over splits or creating wide return paths with high loop inductance. Anything other than a wide plane means more crosstalk between signal paths sharing this return conductor. a wide, continuous ground plane adjacent to a signal trace will be the lowest crosstalk configuration. plane grounding utilizes a large, continuous ground plane layer within the pcb stackup. the best way of minimizing ground impedance in a multicard system is to use another pcb as a backplane for.
From www.researchgate.net
Stacked layers of a superconducting Nb ground plane, Xand Y Continuous Ground Plane the best way of minimizing ground impedance in a multicard system is to use another pcb as a backplane for. Anything other than a wide plane means more crosstalk between signal paths sharing this return conductor. a wide, continuous ground plane adjacent to a signal trace will be the lowest crosstalk configuration. plane grounding utilizes a large,. Continuous Ground Plane.
From jhdpcb.com
The Role And Design Guidelines Of PCB Ground Plane. Jhdpcb Continuous Ground Plane Anything other than a wide plane means more crosstalk between signal paths sharing this return conductor. with the split ground design, i'm concerned about the gate drive currents (that keep the bootstrap capacitors charged) causing. plane grounding utilizes a large, continuous ground plane layer within the pcb stackup. This eliminates the possibility of routing over splits or creating. Continuous Ground Plane.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Ground and Power Planes PowerPoint Presentation, free download Continuous Ground Plane with the split ground design, i'm concerned about the gate drive currents (that keep the bootstrap capacitors charged) causing. The recommended practice is to use a solid (continuous) ground plane on layer 2, assuming layer 1 is used for the. plane grounding utilizes a large, continuous ground plane layer within the pcb stackup. Anything other than a wide. Continuous Ground Plane.
From www.researchgate.net
(a) Interdigital loaded ground plane (Ramachandran et al., 2016), (b Continuous Ground Plane This eliminates the possibility of routing over splits or creating wide return paths with high loop inductance. Anything other than a wide plane means more crosstalk between signal paths sharing this return conductor. the best way of minimizing ground impedance in a multicard system is to use another pcb as a backplane for. with the split ground design,. Continuous Ground Plane.
From www.researchgate.net
A dipole array backed by a ground plane in the presence of a dielectric Continuous Ground Plane a wide, continuous ground plane adjacent to a signal trace will be the lowest crosstalk configuration. however, for high speed/high frequency boards, it is highly recommended to use a continuous ground plane with no splits in each ground layer. The recommended practice is to use a solid (continuous) ground plane on layer 2, assuming layer 1 is used. Continuous Ground Plane.
From slideplayer.com
Ground and Power Planes ppt download Continuous Ground Plane The recommended practice is to use a solid (continuous) ground plane on layer 2, assuming layer 1 is used for the. plane grounding utilizes a large, continuous ground plane layer within the pcb stackup. a wide, continuous ground plane adjacent to a signal trace will be the lowest crosstalk configuration. however, for high speed/high frequency boards, it. Continuous Ground Plane.
From eigo-bunpou.com
Explicación detallada de “ground plane”! Significado, uso, ejemplos Continuous Ground Plane The recommended practice is to use a solid (continuous) ground plane on layer 2, assuming layer 1 is used for the. a wide, continuous ground plane adjacent to a signal trace will be the lowest crosstalk configuration. however, for high speed/high frequency boards, it is highly recommended to use a continuous ground plane with no splits in each. Continuous Ground Plane.
From beyonddesign.typepad.com
Free Download Navisworks Ground Planes Beyond Design the Continuous Ground Plane The recommended practice is to use a solid (continuous) ground plane on layer 2, assuming layer 1 is used for the. Anything other than a wide plane means more crosstalk between signal paths sharing this return conductor. the best way of minimizing ground impedance in a multicard system is to use another pcb as a backplane for. a. Continuous Ground Plane.
From library.vuforia.com
Introduction to Ground Plane in Unity VuforiaLibrary Continuous Ground Plane a wide, continuous ground plane adjacent to a signal trace will be the lowest crosstalk configuration. This eliminates the possibility of routing over splits or creating wide return paths with high loop inductance. Anything other than a wide plane means more crosstalk between signal paths sharing this return conductor. however, for high speed/high frequency boards, it is highly. Continuous Ground Plane.
From www.youtube.com
Effect of ground planes monopole antennas. 20/62 UPV YouTube Continuous Ground Plane with the split ground design, i'm concerned about the gate drive currents (that keep the bootstrap capacitors charged) causing. This eliminates the possibility of routing over splits or creating wide return paths with high loop inductance. The recommended practice is to use a solid (continuous) ground plane on layer 2, assuming layer 1 is used for the. plane. Continuous Ground Plane.
From www.researchgate.net
The groundplane geometry for spotlightmode SAR. Download Scientific Continuous Ground Plane This eliminates the possibility of routing over splits or creating wide return paths with high loop inductance. plane grounding utilizes a large, continuous ground plane layer within the pcb stackup. with the split ground design, i'm concerned about the gate drive currents (that keep the bootstrap capacitors charged) causing. a wide, continuous ground plane adjacent to a. Continuous Ground Plane.
From www.youtube.com
Fusion 360 Electronics 11 Layout Ground Plane and Autorouting YouTube Continuous Ground Plane the best way of minimizing ground impedance in a multicard system is to use another pcb as a backplane for. a wide, continuous ground plane adjacent to a signal trace will be the lowest crosstalk configuration. with the split ground design, i'm concerned about the gate drive currents (that keep the bootstrap capacitors charged) causing. This eliminates. Continuous Ground Plane.
From resources.altium.com
Understanding 2Layer PCB Ground Planes PCB Design Blog Altium Continuous Ground Plane with the split ground design, i'm concerned about the gate drive currents (that keep the bootstrap capacitors charged) causing. however, for high speed/high frequency boards, it is highly recommended to use a continuous ground plane with no splits in each ground layer. The recommended practice is to use a solid (continuous) ground plane on layer 2, assuming layer. Continuous Ground Plane.
From resources.pcb.cadence.com
What is Discontinuous Grounding in an Electrical System? Advanced PCB Continuous Ground Plane Anything other than a wide plane means more crosstalk between signal paths sharing this return conductor. however, for high speed/high frequency boards, it is highly recommended to use a continuous ground plane with no splits in each ground layer. with the split ground design, i'm concerned about the gate drive currents (that keep the bootstrap capacitors charged) causing.. Continuous Ground Plane.
From www.youtube.com
Workman 5/8 wave ground plane 8ft off the ground YouTube Continuous Ground Plane Anything other than a wide plane means more crosstalk between signal paths sharing this return conductor. the best way of minimizing ground impedance in a multicard system is to use another pcb as a backplane for. plane grounding utilizes a large, continuous ground plane layer within the pcb stackup. however, for high speed/high frequency boards, it is. Continuous Ground Plane.
From www.youtube.com
modified partial ground plane for bandwidth enhancement using hfss Continuous Ground Plane however, for high speed/high frequency boards, it is highly recommended to use a continuous ground plane with no splits in each ground layer. plane grounding utilizes a large, continuous ground plane layer within the pcb stackup. a wide, continuous ground plane adjacent to a signal trace will be the lowest crosstalk configuration. the best way of. Continuous Ground Plane.
From www.researchgate.net
Effect of the large conductive sheet on the ground plane (a) Simulation Continuous Ground Plane the best way of minimizing ground impedance in a multicard system is to use another pcb as a backplane for. The recommended practice is to use a solid (continuous) ground plane on layer 2, assuming layer 1 is used for the. This eliminates the possibility of routing over splits or creating wide return paths with high loop inductance. Anything. Continuous Ground Plane.
From www.researchgate.net
5 Dimensions of base ground planes (a) planar top view, (b) planar Continuous Ground Plane with the split ground design, i'm concerned about the gate drive currents (that keep the bootstrap capacitors charged) causing. a wide, continuous ground plane adjacent to a signal trace will be the lowest crosstalk configuration. the best way of minimizing ground impedance in a multicard system is to use another pcb as a backplane for. The recommended. Continuous Ground Plane.